
In today’s world, clean air is more than a luxury, it’s a necessity as we spend al lot of our time indoors. According to EPA.gov, indoor air pollution may be 2 to 5 times more polluted than outside. This article will discuss what a HEPA filter is, how it works, and its benefits.
The Science Behind HEPA Filters
A HEPA filter is a type of air filter. It stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air. It can remove 99.97% – 99.99% of airborne particles as small as 0.3 microns.
They are constructed from a dense mat of fibers arranged in a random pattern. These fibers are typically composed of fiberglass, which creates a maze-like structure capable of trapping particles with high efficiency.
HEPA filters undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet strict standards set by organizations such as the United States Department of Energy (DOE) and the European Union (EU).
An inch = 25400 microns (µm). For comparison, here is a list of objects and how large they are in microns:
- Bacterial cells range from 1 – 10 microns.
- A single strand of human hair ranges from 50 – 10 microns.
- Dust mites are about 400 microns
- Viruses are typically less than 0.1 microns
- Smoke particles range from 0.01 – 0.1 micron
- Pollen generally range from 10 to 1000 microns.
How HEPA Filters Work
HEPA filters operate through three key mechanisms:
Interception: Large articles are captured when they come into contact with the fibers of the filter.
Impaction: Medium-sized particles collide with the fibers, becoming trapped.
Diffusion: Smaller particles that randomly move through the air flow collide with gas molecules, causing them to stick to the fibers and become trapped.
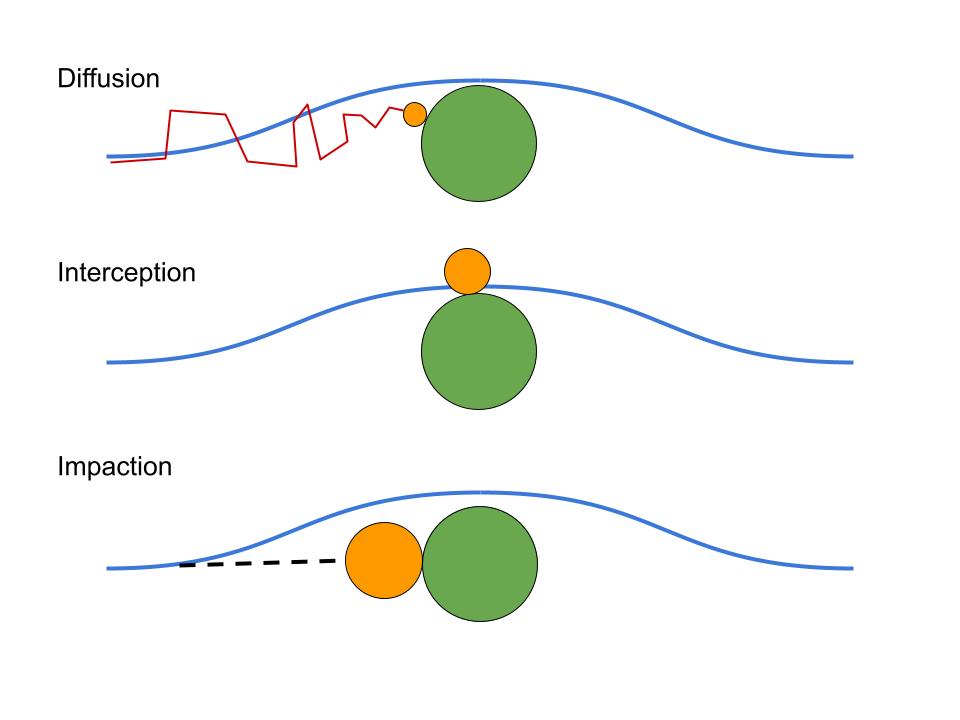
The blue line represents the air flow, the orange circle represents the particle, the green circle represents the fiber, and the red line represents the random pathing caused by the gases which causes the particle to be trapped by the fiber.
Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values, or MERVs
Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values, or MERVs reports how effective a filter is at capturing particles between 0.3 to 10 microns (µm).
This is useful for comparing different filter performance. Below is a list of MERV ratings with its efficiency at different particle sizes (derived from EPA):
- Rating 1-4: 3 – 10 microns = <20%
- Rating 6: 3 – 10 microns = 49.9%
- Rating 8: 3 – 10 microns = 84.9%
- Rating 10:
- 1 – 3 microns = 50% – 60%
- 3 – 10 microns = >85%
- Rating 12:
- 1 – 3 microns = 80% – 89.9%
- 3 – 10 microns = >90%
- Rating 14:
- 0.3 – 1 microns = 75% – 84%
- 1 – 3 microns = >90%
- Rating 16: 0.3 – 1 microns = >75%
Benefits of HEPA Filters
Allergens: HEPA filters trap pollen or particles that triggers an allergic response. Asthma and allergy-sensitive individuals benefit from reduced exposure to allergens, leading to fewer symptoms and improved respiratory health.
Pet Dander: HEPA filters remove pet dander from the air, making homes more comfortable for pet owners and allergy-sensitive individuals.
Mold: By trapping mold spores, HEPA filters help prevent mold growth and mitigate associated health risks.
Smoke: HEPA filters are highly effective at capturing smoke particles, as well as pollutants such as fine dust and airborne chemicals.
It’s important to note that HEPA filters don’t remove odors. Instead, activated carbon filters are the filters made to filter out odors.
Applications of HEPA Filters
HEPA filters are used in various settings. They are used in technologies such as air purifiers or vacuum cleaners:
Residential Use: Homes and apartments benefit from HEPA-filtered air for a cleaner and healthier living environment.
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, clinics, and laboratories rely on HEPA filters to maintain sterile environments and prevent the spread of airborne pathogens.
Commercial Spaces: Offices, schools, and public buildings use HEPA-filtered air to enhance occupant comfort and productivity.
Industrial Settings: Cleanrooms, manufacturing facilities, and pharmaceutical plants utilize HEPA filters to ensure product quality and worker safety.
Conclusion
HEPA filters are essential components in air purification systems. Their ability to trap allergens, pollutants, and even microscopic particles makes them a great tool for maintaining clean and healthy indoor environments.
References
Albers, K. (2022, September 23). What is a HEPA filter & how does it work? | ISO-Aire. ISO-Aire Air Purifiers. https://www.iso-aire.com/blog/what-is-a-hepa-filter-and-how-does-it-work
How HEPA filters work – BOFA. (2022, January 21). BOFA. https://bofainternational.com/us/how-hepa-filters-work/
Precision Machined Products Association. (n.d.). Thickness of a human Hair – Precision Machined Products Association. Precision Machined Products Association – Helping the Precision Machined Industry Adapt & Thrive. https://www.pmpa.org/tag/thickness-of-a-human-hair/#:~:text=A%20human%20hair%20can%20be,and%20a%20meter %20in%20millionths
Water Quality Association. (2023, July 3). Bacteria & Virus – Water Quality Association. https://wqa.org/resources/bacteria-virus/#:~:text=Bacterial%20cells%20range%20from%20about,human s%2C%20while%20others%20are%20harmful.
What is a HEPA filter? | US EPA. (2024, March 5). US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/what-hepa-filter
What is a HEPA Filter & How Does It Work? | Sylvane. (n.d.). Sylvane. https://www.sylvane.com/what-is-a-hepa-filter-how-does-it-work.html
What you need to know about HEPA filters. (n.d.). MMM-ext. https://www.filtrete.com/3M/en_US/filtrete/home-tips/full-story/~/how-to-reduce-dust-mites/?storyid=75200b03-7977-4621-a248-b5bc0d4e1ae2
The inside story: A guide to indoor air quality | US EPA. (2023, June 22). US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/inside-story-guide-indoor-air-quality#:~:text=EPA’s%20Total%20Exposure%20Assessment%20Met hodology,rural%20or%20highly%20industrial%20areas.